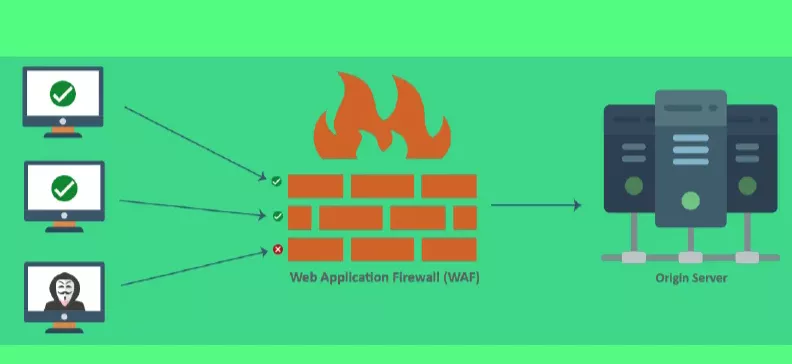
Among the plethora of cyber-attacks in the online space, the security of websites and web applications holds paramount importance. One of the key tools for this purpose is known as WAF. WAF, short for Web Application Firewall, acts as a defensive barrier between web servers and internet traffic, allowing only authorized and secure traffic to reach the server.
In the following, we elaborate further on what WAF is, its types, and how it protects web servers against cyber-attacks. If you intend to purchase a WAF, it’s advisable to read this article before taking any action.
Understanding WAF: A Defensive Barrier Against Cyber-Attacks
In response to the question “What is WAF?” it can be said that this phrase stands for Web Application Firewall. More precisely, WAF is a type of device or software designed to protect websites and web applications against cyber-attacks. By monitoring HTTP and HTTPS traffic, WAF identifies and blocks attacks before they harm your system. Through the use of a web application firewall, only authorized and secure traffic will access the server.
It’s important to note that relying solely on a web application firewall for security is not sufficient; other security measures such as purchasing SSL are necessary for encrypting data transmitted between the user and the server.
Types of WAF: 3 Structural Types for Establishing Security in the Online Space
WAF architecture can be divided into three types based on implementation. Each of these types of web application firewalls has its specific features. Below, we explain these three types further:
Network-based WAF: Network-based web application firewalls are usually installed on-premise and locally. Network-based WAFs provide the highest level of security. They are also considered the most expensive type of WAF and require costly maintenance of physical equipment. Host-based WAF: One type of WAF is host-based. These WAFs are installed as software on web servers and offer greater flexibility and lower cost compared to other types of WAFs. Cloud-based WAF: These types of WAFs are offered as cloud services and are suitable for environments with limited resources. Cloud-based WAFs do not require initial capital and users can subscribe to this type of service by paying for a long-term subscription.
How Does a Web Application Firewall Work?
You’ve likely understood what WAF is by now, and now you may be wondering, “How does WAF work?” WAF identifies and neutralizes potential attacks by examining and filtering incoming traffic to the web server. This process includes the following:
Traffic analysis: WAF analyzes traffic patterns through a series of complex processes to identify suspicious activities. Rule execution: Based on a set of defined rules, WAF determines which requests are safe and which should be blocked. Blocking attacks: Upon detecting an attack, WAF quickly blocks malicious requests. The process of blocking attacks requires strong support from the network and server support team to ensure that WAF is properly configured and maintained. Additionally, this process is essential for resolving any technical issues that may arise during WAF operation.

What Types of Cyber-Attacks Does WAF Protect Against?
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are designed to protect web applications from various types of cyber-attacks. Here are some of the most important attacks that WAF can protect against:
SQL Injection (SQLi) Attack: This attack occurs when an attacker sends malicious SQL code through web forms to access or manipulate databases. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attack: In these attacks, attackers inject malicious JavaScript or other scripts into victim web pages, which can lead to theft of sensitive information. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Attack: This type of attack occurs when a legitimate user unknowingly executes commands determined by the attacker. File Inclusion Vulnerabilities Attack: This type of attack includes Local File Inclusion and Remote File Inclusion, where attackers add or execute malicious files on a web server. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Attacks whose goal is to disable a web server by sending heavy and unusual traffic. Session Hijacking and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: In these attacks, attackers attempt to control communication between two parties without their knowledge. Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that exploit unknown vulnerabilities in software. Path Traversal and Directory Traversal Attacks: These attacks allow attackers to bypass security restrictions and access files on the server that should not be accessible. WAFs help block these types of attacks by analyzing web traffic and identifying malicious patterns. It’s worth noting that cloud-based WAFs can help reduce server loads and provide better scalability, making them effective against more complex attacks. In this regard, having more information about what cloud is will help better understand how cloud-based WAFs work.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WAF
Using a web application firewall has specific advantages and disadvantages that awareness of them helps better understand this tool and decide to buy WAF. Some of the advantages of WAF include:
Prevention of web attacks: WAF protects web applications against common cyber-attacks. Reduced security risks: By preventing unauthorized access and attacks, WAF helps maintain data security and privacy. WAF acts as an additional layer of security and prevents many security threats from occurring. Compliance with security standards: Using WAF helps organizations comply with security standards such as PCI DSS. Precise control over web traffic: It’s possible to set precise rules for controlling user access to the website. Alongside these advantages, WAF has some disadvantages that should be noted. These include:
Complex management: Configuring and managing WAF can be complicated, especially for organizations with limited technical knowledge. High costs: Some WAFs may have high costs for purchasing and maintenance. Possibility of false positives: WAFs may sometimes mistakenly identify legitimate traffic as a threat, which can disrupt normal website operations. Limitations against complex attacks: WAFs may not be entirely effective against some more complex attacks or emerging tactics.
